If you want your Google rankings to go from barely visible to top of the Serps, working methodically through an SEO priority list will keep your campaigns on track.
Websites optimized for SEO enjoy long-term free-flowing traffic.
In turn, that means more conversions, leads, and revenue for your business.
If you studied business, you might have heard of Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs.
I transformed what I consider important in SEO into an SEO priority list pyramid to guide SEOs.
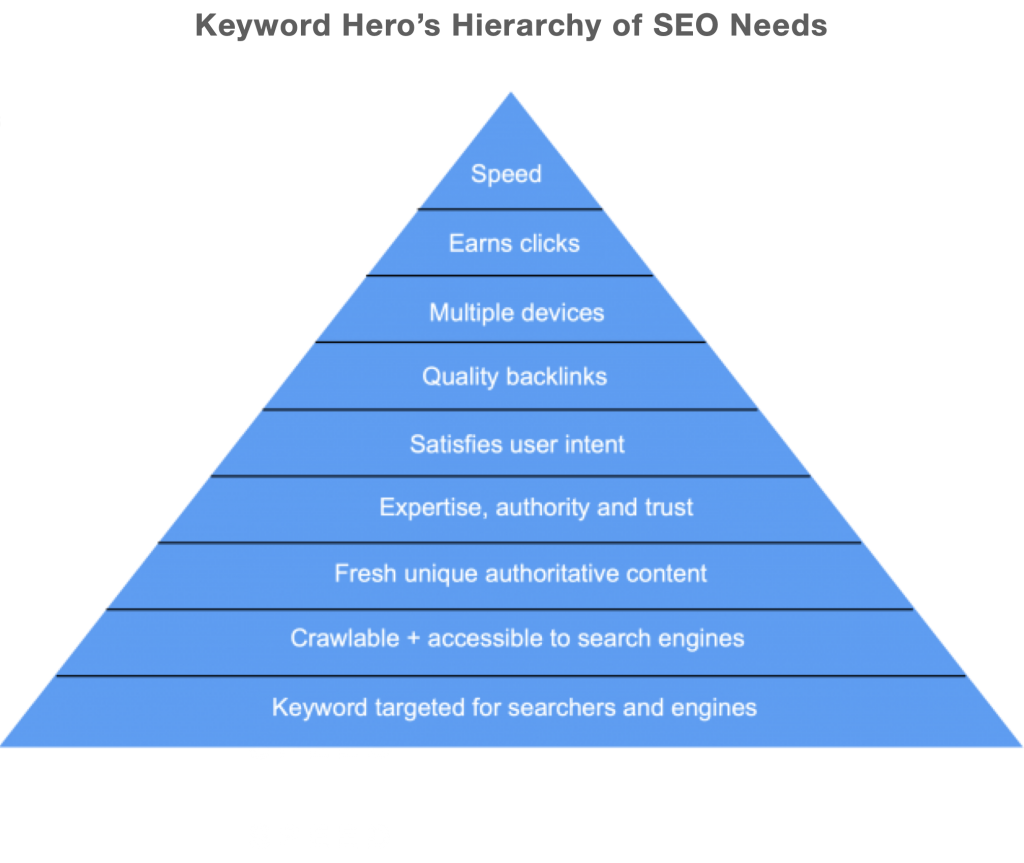
1. Keyword targeted
Probably the most important element of an SEO strategy is knowing your conversion keywords. The below statistics compiled by Ahrefs illustrate this point.
- 68% of online experiences begin with a search engine. Source BrightEdge
- 0.78% of Google searchers click on results from the 2nd page. Source Backlinko
- 53.3% of all website traffic comes from organic search. Source BrightEdge
- 92.96% of global traffic comes from Google search, Google Images, and Google Maps. Source Sparktoro
- SEO drives 1000%+ more traffic than organic social media. Source BrightEdge
- 69.7% of search queries contain four words or more. Source Ahrefs
Improving keyword targeted traffic can be done by using focus keywords relevant to rank for specific search queries.
These can be long-tail keywords or head terms.
You should pan for gold where there is less competition and more opportunity to increase visibility on Google.

Hence, by correctly identifying your conversion keywords, you can improve performance in both paid and organic marketing.
First, we need to do some keyword research.
Once we know what keywords to target we can implement a growth plan in areas with the highest traffic potential, where competition is less fierce.
Accordingly, keyword optimization will unlock new traffic streams.
Understanding where your biggest untapped traffic source is crucial.
Indeed, small changes can have a profound impact by finding the low hanging fruit of organic search results.
Unblocking keywords (not provided) on Google Analytics is the first step.
How do I get my keywords back?
You can recover your organic keywords, in seven steps.
Step 1: Pull together nine different data sources
Step 2: Perform Google Analytics data analysis
Step 3: Analyze organic traffic for keyword fluctuation in Google Serps
Step 4: Train the keyword classifications
Step 5: Match sessions with keywords using an algorithm
Step 6: Start computation to unlock keywords
Step 7: Match session vs. string
Read in detail how we unblock (not provided)
Once you have your keywords back again you can do the following.
- Understand conversion keywords
- Find out keywords for quick wins
- Access keyword performance across devices
- Stop ranking cannibalism
- Analyze long-tail keywords
- Build better content
- Adjust to Google’s algorithm updates
- Detect and monitor brand keywords
2. Crawlable + accessible to search engines
One crawlability.
A Google web crawler can look at a web page much like you would if you were browsing content on the web.
They go from link to link and bring data back to Google’s servers.
Thus, crawlability describes the search engine’s ability to access and crawl content on a page.
Consequently, if a site has no crawlability issues, a Google website crawler can access all its content easily, by following links between pages.
However, broken links or dead ends might result in crawlability issues–the search engine’s inability to access specific content on a site.
On the other hand, indexability refers to the search engine’s ability to analyze and add a page to its index.
In fact, even though Google could crawl a site, it may not necessarily be able to index all its pages, typically due to indexability issues.
What affects website crawlability?
- Site structure. Pages that aren’t linked to or from anywhere else.
- Internal link structure. A good internal link structure will allow Google site crawlers to quickly reach pages deep in your site. A poor structure, however, which leaves the Google site crawler at a dead end, results in the web crawler missing some of your content.
- Looped redirects. Broken pages stop site crawlers in their tracks, resulting in crawlability issues.
- Server errors. Broken server redirects and many other server-related problems may prevent web crawlers from accessing all of your content.
- Blocking web crawler access. You can deliberately block web crawlers from indexing certain pages on your site. And you may want to do this to restrict public access.
3. Fresh unique and authoritative content
Without unique and useful content, your chances improving key SEO metrics will diminish. To make tracking and improving those key SEO metrics easier, it’s essential to use the right SEO tools. Platforms like SEMrush, SimilarWeb, AccuRanker, Ahrefs and other SEO platforms similar to Ahrefs give you valuable data on keywords, backlinks, and traffic performance and help to monitor rankings and discover optimization opportunities that help your content grow steadily.
Search engines access how valuable your content is depending on how people engage with the content. So, if your blog posts have a high bounce rate and a low average time-on-page, Google might assume that the content is not of much value to people or at least for that particular search term.
Thus, your content needs to be well written and entertaining and match the intent of the search targeted keyword.
However, you can hit a jackpot writing content that reveals an unmet need. This involves doing surveys, questionnaires, and asking your customers directly. A 30-minute customer interview can glean significant insight into your target audience. Of course, customers are busy too, so you might need to offer a reward, whether that is the first peek at a new product or entry into a prize draw. Amazon vouchers are always well received.
Hence, to become an authority on a subject matter, you will need to show your readers that you have a deep understanding of the subject matter in question. Can you surprise and delight your readers with something they never thought about before?
In today’s digital landscape, where AI-generated content is becoming increasingly common, it’s crucial that your writing maintains a natural, engaging tone that resonates with real people. If you’re using AI tools to assist with content creation, consider using a AI Text tool like Humanize to ensure your content doesn’t sound robotic or mechanical. Remember, 48% of consumers immediately tune out when content feels too automated – and search engines are getting better at recognizing and potentially downranking content that lacks that human touch.
First, try to think of one thing that will improve their lives / business that is related to your product and you will be on the right track.
You absolutely need to know what search terms people are actually using to find you on Google. I mean, how else are you going to create content that meets them where they are?
Building authority doesn’t happen overnight – it’s more like growing a garden than flipping a switch. But if you keep showing up with genuinely helpful content, your audience will grow. And the best part? They’ll start coming to you first when they need answers in your space.
4. Expertise, authority and trust

Building on the last point, expertise, authority, and trust is a feast for Google’s eyes.
So much so that they coined it Google EAT.
Remember that the first criteria for a page’s quality rating is whether the purpose of the page is clear.
Therefore, websites without a clear benefit to visitors, including pages that make no attempt to help users, or sites that spread hate, cause harm or misinform users, receive the lowest ratings.
Knowing the keywords used to get to a particular landing page is a good way to align content with search intent.
To rank on Serps, the level of expertise, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness (EAT score) is very important.
Google EAT guidelines
- The expertise of the creator of the main content, e.g. a legal instruction video made by someone with no clear expertise, perhaps someone without a legal qualification, would receive a low EAT score
- The authoritativeness of the creator of the main content, the main content itself, and the website e.g. legal information on a surfing website would score badly
- The trustworthiness of the creator of the main content, the main content itself, and the website e.g. a shopping checkout page that has an insecure connection would not get a good EAT score
The quality of the content is an important consideration for page quality rating.
Google considers content to be low quality if it is created without adequate time, effort, expertise, or skill.
Indeed, pages with low-quality main content usually fail to achieve their purpose.
Informational pages with inaccurate main content get poor ratings.
If the main content is difficult to read, watch, or use, and it takes effort to understand and use the page then it will not be deemed high quality.
Broken functionality of a page due to poor design, structure, or lack of maintenance diminishes the quality rating of the page.
The title of a page should always describe the content. A title that asks is climate change a hoax, should not appear on a cooking recipe website.
5. Satisfies user intent
When new entrants to the world of SEO choose target keywords, they usually go for search terms with the highest volumes.
However, the intent behind the search is a more important factor than the number of searches.
This is often disregarded when content is created. It’s important to rank for a keyword but the content has to be relevant and also satisfy user intent.
There has been a lot of studies conducted into understanding the intent behind a query, and this is reflected by the types of results that Google displays.
The three primary classifications of search intent are ‘do’, ‘know’, and ‘go queries’.
- Do. When a user performs a ‘do’ query, they want to perform a specific action, such as book a flight or buy shoes. These are important to e-commerce websites for example, where a user may be looking for a specific brand or item.
- Know. A ‘know’ query is an informational query, where the user wants to learn about a particular subject e.g. what is the meaning of life?
- Go. These are typically brand queries, where a user is looking to go to a specific website or location. If a user is specifically searching for ‘Adidas high top trainers’, serving her Puma, as a result, wouldn’t meet her needs.
if your result matches user intent you will receive a ranking boost.
Fundamentally, fulfilling search intent is Google’s primary objective.
So if you want to enhance SEO performance, optimizing for search intent needs to be central to your tactics.
Google is obsessed with search intent so your website should be clear.
Therefore, the content has to match the search terms.
And users need to get what they want when they visit.
For example, if a person searching for the meaning of life ends up on a website that sells mountain climbing equipment, his intent has not been satisfied.
Unless of course, the meaning of life is to go mountain climbing, which some climbing enthusiasts might well argue.

6. Quality backlinks
Striving for high-quality backlinks has always been a goal for SEO professionals.
What is a backlink? A backlink is a link created when one website links to another.
In other words, backlinks are inbound links.
Backlinks are important to SEO because they help build your website’s domain and page authority, which contributes to Google’s search result rankings.
Consequently, guest blogging and writing great content on your website are two ways to secure and build high-quality backlinks.
Thus, if you want to land on the elusive first page of search results, you will need at least a few backlinks.
Case studies, surveys, and commenting on 3rd party blogs are also important backlink tools.
7. Made for multiple devices
When designing your website and its main content, choosing a responsive design suits SEO much better.
Sites that use responsive design (one Url for all devices) are more search engine friendly.
A central part of this is because your website will ‘flow’ from device to device.
Understanding your audiences’ multi-device habits is a critical step to implementing an effective SEO strategy.
As we’ll come to later, speed plays a crucial role in all of this.
Improvements to page speed will improve user experience (UX) and influence Google rankings and conversions.
Keywords change too. Keywords rank differently on mobile compared to desktop Serps. And, this will impact your keyword conversion goals.
As we discussed earlier, identifying user intent is important so that you can use keyword optimization to tailor page content to search results, and reduce bounce rates.
Once you’ve got your not provided keywords back you can map out user intent by keyword / device.
8. Earn more clicks
You can see in the below bar chart that company websites (site-links) make up just 21.9% of search results.
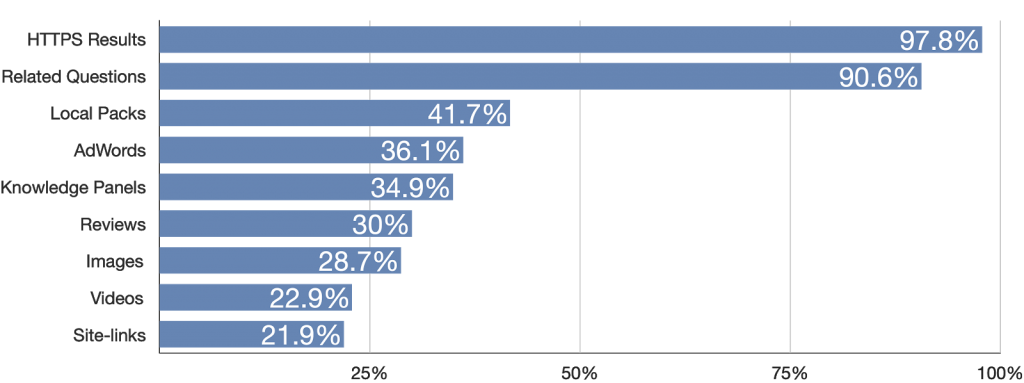
Then there are knowledge panels (34.9%), customer reviews (30%), etc.
So you can see that you have to try many different avenues to earn organic clicks.
As long as you appear somewhere on the first page, you get a decent click-through rate.
And your SEO ROI for keywords will improve.
You can even count on clicks on the second page.
As mentioned before, Google says that the deciding factor in terms of CTR is always its relevance to the user’s intent.
The search result gets more clicks (and is ranked higher) when more people click on the result.
How to improve CTR in Google Search?
There are three ways to do this.
- Create informative content
- Build content valuable enough for a user to click on the search result
- Make visually appealing and compelling content
As we touched on previously, it is users who decide which content is relevant or not.
If you want to improve your CTR, you have to make sure that your content matches the search queries of your users.
9. Speed
At the top of SEO priority list is page speed.
However, speed can also indirectly affect rankings based on bounce rates and dwell time.
Google’s PageSpeed Insights tool is a powerful ally in this regard, and should be closely monitored.
In brief, page speed scores are divided into three categories, slow (0-49), average (50-89), and good (90-100).
If you’re under 50, you have some issues that need to be addressed!
What is bounce rate?
Bounce rate is an important metric that highlights the percentage of visitors who come to your website and leave.
Most bouncers go back to their previous search results or they click the ‘x’ on the tab if they don’t like your page.
If your bounce rate is high, this will negatively affect SEO results.
In Google’s eyes, a high bounce rate equates to poor content or mismatched content and user intent.
For that reason, many SEO professionals have started focusing their time on content marketing.
By demanding high-quality content from websites, Google has not only provided people with more richly informative and relevant websites to meet their needs, but it has improved the overall quality of content across the internet.
What is dwell time?
Dwell time is the amount of time a visitor spends on a single page after clicking a link on Google before they return to the results page.
Sounds a lot like bounce rate.
Where dwell time is the amount of time spent on a web page, the bounce rate is the percentage of visitors who visit a page but then return to the results page without visiting other pages.
Regardless of how much time a visitor spends on your site, if they fail to click on anything, it is counted as a bounce.
For instance, say you search for “what is the meaning of life” on Google.
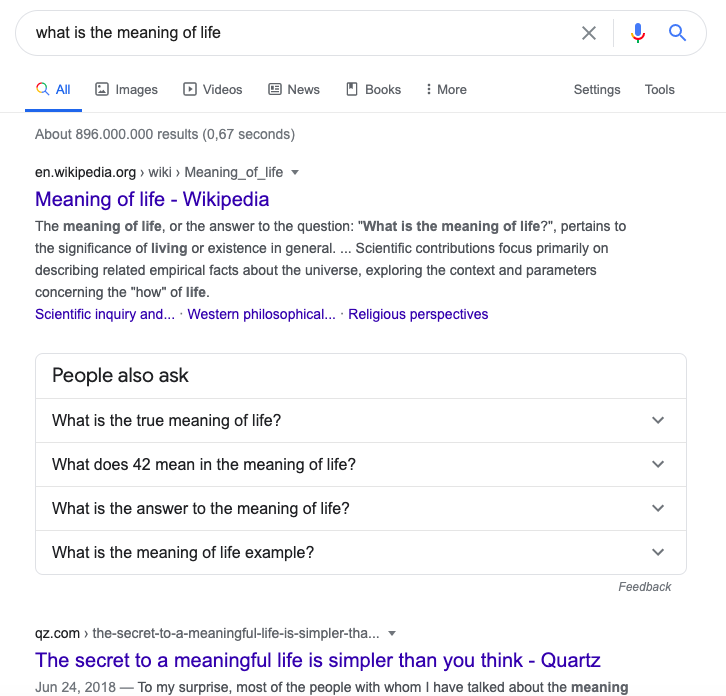
You avoid Wikipedia because you have found it to be unreliable in the past, so you click on Quartz instead.
You go on to read a 2000 word article in roughly five minutes and Google considers this dwell time.
After reading the content piece, you return to the Serps and don’t click on any other link on the results page.
This action of leaving the site without visiting other pages is counted as a bounce.
Yet the bounce rate doesn’t inform Google if you were satisfied with what you read, that’s where the dwell time comes in and can indicate if a user was engaged with the content or not.
Larry Kim, the founder of WordStream, ran an experiment that illuminates the importance of dwell time in SEO.
He checked WordStream’s positions in the Serps before and after Google introduced RankBrain—Google’s machine learning-based search engine algorithm, introduced in October 2015.
He became a bit obsessed trying to figure out RankBrain stating that “Google wants to find unicorns – pages that have extraordinary user engagement metrics like organic search click-through rate (CTR), dwell time, bounce rate, and conversion rate – and reward that content with higher organic search rankings.”

He discovered that results that have better organic search CTRs are nudged higher up the Serps and get more clicks.
This suggests that pages with high-quality, off-the-charts engagement metrics are going to be the most valuable to your business.
Conversely, pages with below-average time-on-site are the most vulnerable pages in terms of SEO.
Indeed, Google rewards pages with higher dwell time with better rankings.
A quick solution is to fix the pages on your site that are most at risk, the below-average or near average pages.
You can renew or rewrite these pages so that they align better with user intent.
Final thoughts on SEO priority lists
While no one can know for sure how the Google search engine algorithm works, you can have an educated guess based on best estimates.
By working through the different components of Keyword Hero’s SEO pyramid you will, at a minimum, improve the SEO performance of your business.
And, as always we will keep a watchful eye on the latest Google updates to see if anything changes in the future.
If it does I will be sure to let you know.
Thanks for reading.

